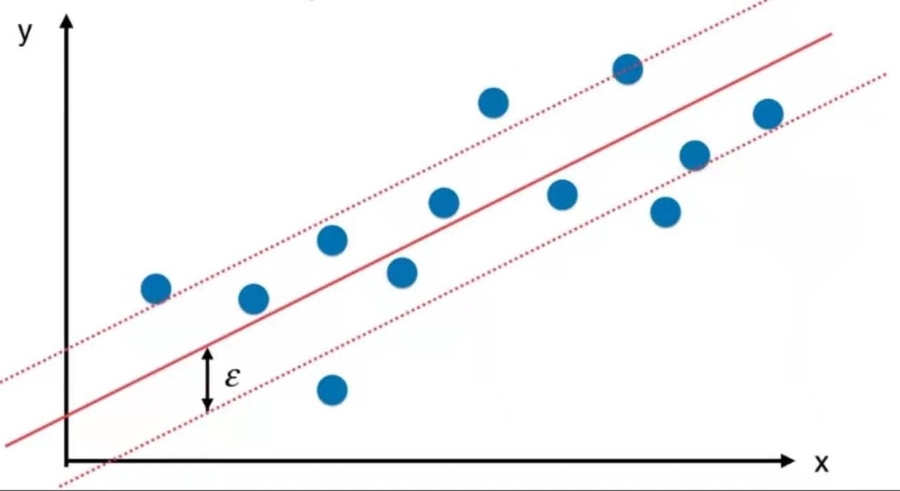
11-9 SVM思想解决回归问题
加载数据
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
boston = datasets.load_boston()
x = boston.data
y = boston.target
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, random_state=666)训练模型
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.svm import SVR
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVR
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
# SVR = Support Vector Regression
# SVR和SVC的用法基本上一样
def StandardLinearSVR(epsilon=0.1):
return Pipeline([
('std_scaler', StandardScaler()),
('linearSVR', LinearSVR(epsilon=epsilon))
])
svr = StandardLinearSVR()
svr.fit(X_train, y_train)
svr.score(X_test, y_test)Last updated