8-2 scikit-learn中的多项式回归和pipeline
准备数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.random.uniform(-3, 3, size=100)
X = x. reshape(-1, 1)
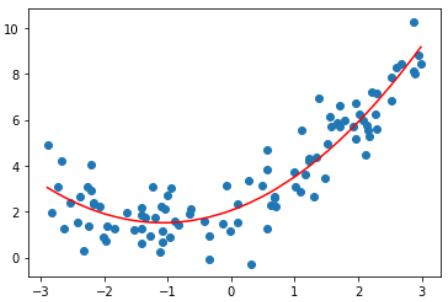
y = 0.5 * x**2 + x + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 1, size=100)使用polynomialFeatures为原数据升维
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
poly.fit(X)
X2 = poly.transform(X)array([[ 1. , -1.34284888, 1.80324311],
[ 1. , -0.18985858, 0.03604628],
[ 1. , -1.58563134, 2.51422675],
[ 1. , 1.2149354 , 1.47606802],
[ 1. , -2.05874706, 4.23843944]])使用scikit-learn中的线性回归算法
关于PolynomialFeatures
假设有x1, x2两个特征,PolynomialFeatures(degree=3),会得到多少项数据?

Pipeline

Last updated