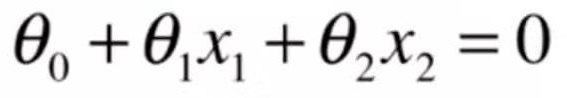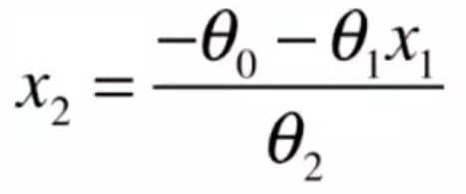9-5 决策边界
绘制决策边界
def x2(x1):
return (-log_reg.coef_[0] * x1 - log_reg.interception_) / log_reg.coef_[1]
x1_plot = np.linspace(4, 8, 1000)
x2_plot = x2(x1_plot)
plt.plot(x1_plot, x2_plot)
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0],X[y==0,1], color='red')
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0],X[y==1,1], color='blue')
plt.show()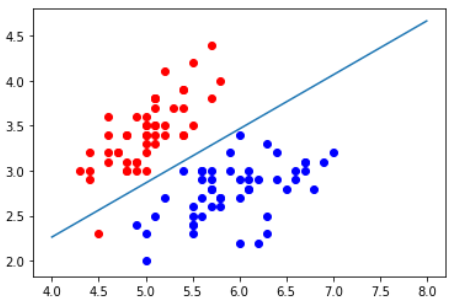
不规则的决策边界的绘制方法
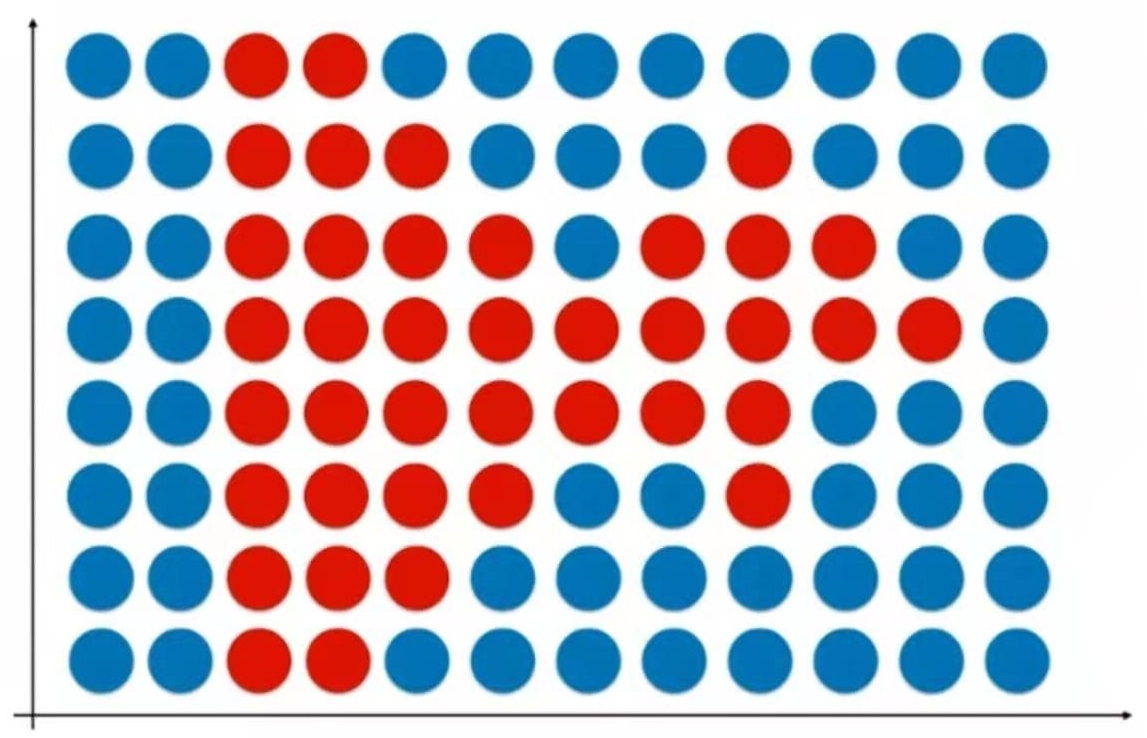
逻辑回归的决策边界

KNN分类算法的决策边界

用KNN对三种iris进行分类的决策边界

用KNN对三种iris进行分类的决策边界, K=50

Last updated